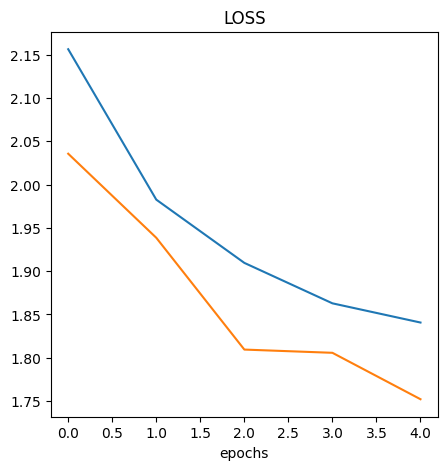
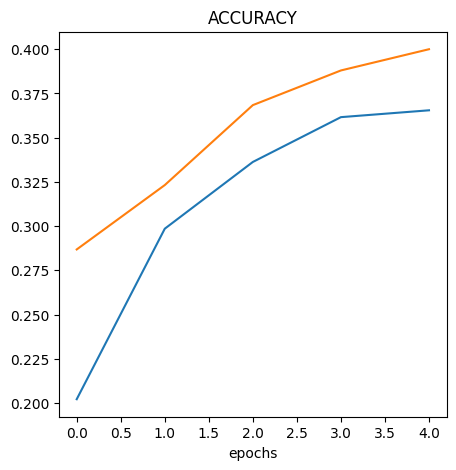
Evaluating Model Loss Curve
Summary
- Visualize the model results
- Understanding what's causing the inaccuracy
- How to resolve the issue
- Get more data
- Simplify the model - reduce # of layers of # of hidden layers
- Generalizing - data augmentation
- Transfer learning
Content
Visualize the Model Results
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
loss = history.history["loss"]
val_loss = history.history["val_loss"]
acc = history.history["accuracy"]
val_acc = history.history["val_accuracy"]
epochs = range(len(history.history["loss"]))
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.plot(epochs, loss)
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss)
plt.title("LOSS")
plt.xlabel("epochs")
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.plot(epochs, acc)
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc)
plt.title("ACCURACY")
plt.xlabel("epochs")
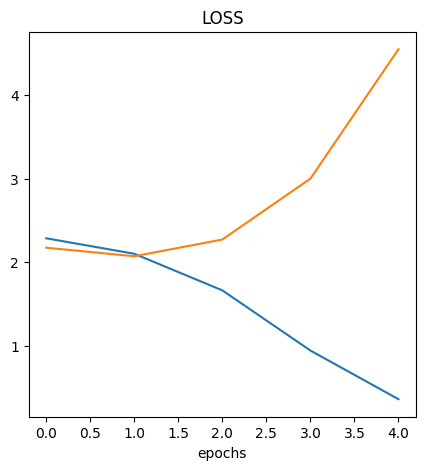
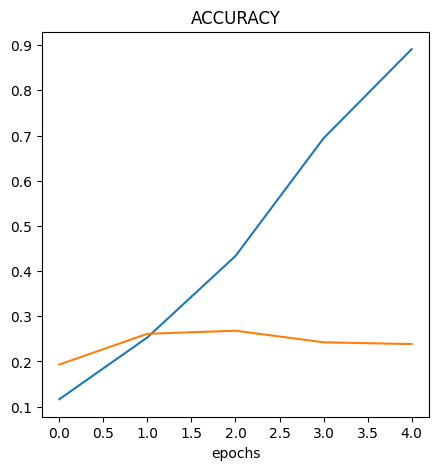
Understanding What's Causing the Inaccuracy
Up to some point the val_loss and val_accuracy follows the loss and
accuracy however, they deviates at some point. This is an indication of
overfitting
How to Resolve the Issue
Data Augmentation
- To avoid overfitting, we can do data augmentation
data_augmentation = tf.keras.Sequential(
[
tf.keras.layers.RandomFlip("horizontal"),
tf.keras.layers.RandomZoom(0.1),
tf.keras.layers.RandomRotation(0.1),
]
)
model = tf.keras.Sequential(
[
tf.keras.layers.Resizing(180, 180),
tf.keras.layers.Rescaling(1.0 / 255),
data_augmentation,
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(10, 3, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(10, 3, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(10, 3, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(10, 3, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(len(class_names), activation="softmax"),
]
)